There are differences in the route which I usually take and the one which GPS shows as the shortest, probably due to the algorithms used. I learned from my graph theory data structure classes that (BFS) Breadth First search example is GPS navigation and digital maps. I tried looking for the possible use of Algorithms (Breadth First Search example or A* application) used in GPS navigation on the web, but I couldn’t find a lot of details. So here is how Breadth First Search is used in real life application like GPS.
Let’s first understand working of GPS navigation
Digital maps, unlike humans, see streets as a bunch of nodes. The 2.6-mile road from the Columbus Circle station (59 st) to Cathedral Pkwy (110 st) is called Central Park West. We (humans) consider this road a single entity (You may divide it into few more segments based on metro stations or intersections, but not more than that).

But a GPS navigation or any other digital map divides it into hundreds of segments, with some only 24 meters long. A GPS looks at this street as a graph divided into vertices and edges.
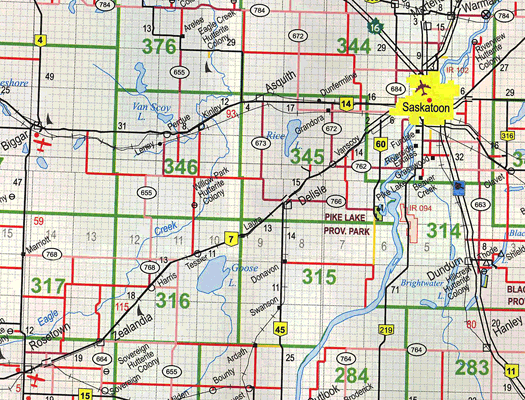
Considering this, there is a lot of data to be covered and calculated while finding the shortest path.
What is a graph?
A graph usually looks like the image below and is made up of vertices and edges (represented by lines and circles, respectively).

The objective of a graph is to represent a problem as a set of points that are connected in various ways using edges. With the help of such graphs, we tend to solve our problems by applying various algorithms.
Let’s take an example to understand better.
Facebook is a good example to understand graph theory.
Facebook has millions of users. If a person needs to find a friend, he can use an array and search. But that would take a lot of time and memory to search for so many people, making the problem quite complex.
But if the same scenario is represented using a graph, the problems tend to get solved easily. With a graph, you know that these two people are actually friends (Though real-life scenarios are not exactly that simple!). Check this video on how graph theory is used in social networks:
Graph theories are frequently used in various other fields, such as maps, e-commerce, and computer games.
Before we go further down this road, read this detailed article about graph theory, which explains other important aspects of Graphs such as Directed, Undirected, Cycle or Loop, and Matrix.
What’s the difference between a Graph and a Tree?
A tree is a special type of graph, i.e., a minimal graph, where there is only one path between two vertices.
So what is Breadth First Search and how does it work?
Depth First Search (DFS) and Breadth First Search (BFS) are algorithms, or in simple terms, they are methods to traverse a graph.
Before I explain Breadth First Search, consider this example.
Take a graph with 13 nodes. When Breadth First Search is applied to this graph, the algorithm traverses from node 1 to node 2 and then to nodes 3, 4, 5, 6 (in green) and so on in the given order.
If you consider 1 (in red) as the first node, you observe that Breadth First Search gradually moves outward, considering each neighboring node first.

This eventually brings us to the accepted definition of the Breadth First Search algorithm:
“Breadth First search (BFS) is an algorithm for traversing or searching tree or graph data structures. It starts at the tree root (or some arbitrary node of a graph, sometimes referred to as a "search key") and explores the neighbor nodes first, before moving to the next level neighbors.”

Graph Traversal in Maps
Take a look at this simple “Gridworld” which is used for various graph traversal algorithms. Your digital map considers your world a similar grid, which is made up of intersections connected to each other.

Now for the grid shown, there could be N number of ways to traverse from point A to point P.
Following are two of these N ways in which one can travel from point A to point P.

So how does an algorithm decide which the shortest way to reach a destination is? Graph Traversal Algorithms!
The Breadth First Search algorithm looks at the map as we do; it just can’t perceive it completely. When you have to travel from one destination to another, you draw a line from point A to point B, and then chose the road closest to that line. Algorithms repeat the same method choosing the node nearest to the intersection points, eventually selecting the route with the shortest length.
Let’s take a simple example of GridWorld given above and try solving it using Breadth First Search. Assume you need to travel from location A to location P.
Note: Every vertex in the image is given a number, which is the total distance from the source and an alphabet which represents the previous node.
Breadth First Search for GridWorld
Step 1 - Visit neighboring nodes to A, i.e, B, E, and F. The vertex to B would become 1-A and since E and F are also at an equal distance as B, hence vertices to both E and F from A, could be denoted as 1-A too.

Step 2 - Mark "A" as visited. Use B as the source node. Visit adjacent nodes to B: C (2B) and G (2B). Node F is already considered.

Step 3 - Visit neighboring nodes of E: I (2E) and J (2E), and mark E as visited.
Step 4 - Visit neighbors of F: K (2F). F is marked as visited.
Step 5 - Repeat until all nodes are visited.
Step 6 - The shortest route from A to P is diagonal with distance 3.

Removing unused vertices creates a minimum spanning tree, where each node is connected to at least one vertex.
But in real scenarios, diagonal movement isn't always possible. Let's analyze GridWorld again, this time disallowing diagonal moves.
Step 1 - Source node A: visit B(1A), E (1A). Mark A as visited.

Step 2 - Node B: visit C (2B) and F (2B), mark B as visited.
Step 3 - Node E: visit I (2E), mark E as visited.

Step 4 - Continue visiting all nodes and marking visited.
Step 5 - Remove unconnected vertices, and build the minimum spanning tree.
Step 6 - Highlight shortest path A to P with a distance of 6.

You now understand why GPS navigation didn't suggest the path A, E, I, M, N, O, P or A,B,C, D, H, L, P though they were equidistant.
Once you've understood the way GPS works, you’d wish the world could be a simple Grid! But to a programmer's disappointment, it isn’t. Hence, for a GPS, distance is not the only factor in choosing a route, rather elapsed time, the speed limit on a route, live traffic update, the number of stop signals all has to be taken into consideration. That’s why you would find your GPS occasionally suggesting winding state highways to travel instead of the usual national highways.
Most of the GPS or digital maps have evolved over Breadth First Search to A* algorithm (You can read more about A* algorithm - Here) due to better complexity over a period of time.
Yet, GPS is one of the most amazing devices. Connected to satellites 12,000 miles above the planet, it calculates your position in real time with more than 50,00,000 possibilities for a particular route.
Watch the video explaining the Use of Breadth first search in GPS navigation here: