Hiring the right talent is crucial to any organization’s growth and success. “By implementing recruiting best practices and supporting technology, you can potentially reduce your time to hire by up to 50 percent, reduce cost per hire by up to 70 percent, and improve recruiter efficiency while finding the talent you need for driving business results.”1
Companies try everything from recruiting agencies to job boards to employee referrals to social media. But the efficacy of these approaches can be often debatable. But that’s a post for another day.
Here, we bring you some sure-fire concepts that will boost hiring efficiency.
Let’s see how exactly it helps.
How many candidates should you interview before making a decision to hire? Imagine a situation where you have a hundred applicants for a position. The problem is that neither will you interview just one candidate nor will you interview all hundred. The dilemma is not whom to pick but how many to even consider before you hire (or you give up).
The most intuitive answer would be that it requires a balance between looking and leaping - that you must look at enough candidates to build a standard and decide on whatever satisfies the established standard. This looks like the perfect answer but here is the catch. Most people can’t say what this standard or balance should be. Luckily, mathematics comes to your rescue and provides the answer. Optimal Stopping Theory...
It is an idea “that every decision is a decision to stop what you are going to make a decision.”2 The theory suggests that you should reject the initial 37% of all the applicants and hire only after that. After this point, you should select the next applicant who is better than all candidates you interviewed before the cutoff. This is not intuition or a compromise between looking and leaping. It is a probable result.

Here look at this example if you have five weeks to choose a primary contractor. You could expect to see possibly four a week; that is an anticipated total of 20 suppliers. If you selected normally and selected the first ‘good enough’ option, the probability of finding the optimum supplier is just 5%. However, if you rejected the first 37% suppliers, in this case, 18 suppliers, and then selected the next supplier that was better than all the previous suppliers, then your odds of selecting the optimum supplier would increase to 40% (For the more curious people, go here to read about the famous example, the Secretary problem.)
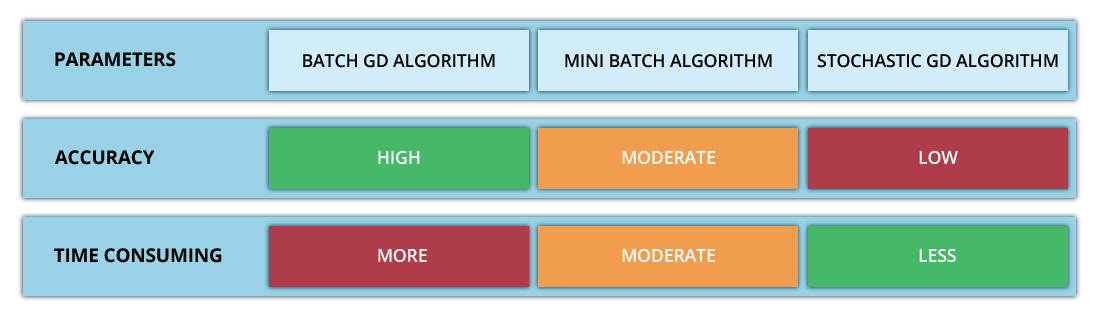
This is just one of the mathematical theories that can help recruiters. To list a few more, there is Negativity Threshold which can help you identify the candidates that are inconsistent in their interview answers or are withholding information. Negativity Threshold was presented by Hannah Fry in her TED talk “The Mathematics of Love.” It was coined by John Gottman by observing how couples interact with each other.
The equations look something like this:
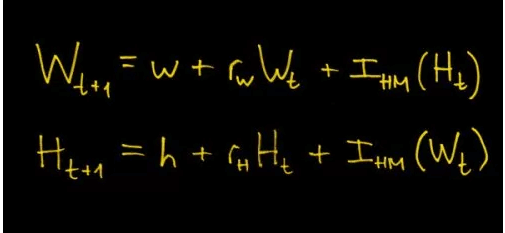
The left-hand side of the equation tells how positive or negative a wife/husband will be in the next thing she/he says. Here, w is the mood of the wife in general, r_w.W_t is the mood of the wife when she’s with her husband and I_(HM) is the influence that her husband’s actions will have on her. Researchers have plotted the effects the two partners have on each other. The plot looks as follows:
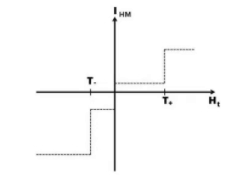
Here, the term T_ is the negativity threshold. At this point, the husband’s negative impact becomes so high that the wife responds with more negativity. To know more about this theory you can watch [ted talk link] or read this.
The negativity threshold suggests you be upfront about any issues and get all sorts of concerns out in open to avoid issues further down the line.
Another interesting equation that is worth looking at is The Drake Equation. The equation was conceived in 1961 by Dr. Frank Drake in an attempt to find the number of potential extraterrestrial bodies with life in the universe. He took something extremely complex and daunting and broke it down into something easy to understand. The Drake equation looks something like this:
The equation involves various factors such as the average rate of star formation in our galaxy, the fraction of stars that have formed planets, and much more which we will not get into. But, what how does this apply to hiring practices? A very obvious similarity is that both use data to pinpoint something or “someone” out there.
An important step in hiring candidates is determining the business factors your company wants to improve, says Emilio J. Castilla, Nanyang Technological University professor of management at the MIT Sloan School of Management. Determining these factors brings clarity to the business and helps everyone understand their roles. For instance, there is something called Sales Velocity, defined as:
This equation does not help in identifying the top performers but also helps in determining the areas where an individual needs to improve. Drake’s theory is extremely useful when it comes to bringing order to a chaotic world.
Although most of the recruiting process is often dominated by emotion, mathematics is the one subject which can be applied everywhere, even hiring, without this particular bias.
Can you math enthusiasts think of any more? Let us know in Comments.
& for some of you who are super busy or are less inclined to "appreciating" math concepts, let us do the work for you.
Take a free trial for our Online Assessment software to hire the best mathematician (or developers) in your talent pipeline
Companies try everything from recruiting agencies to job boards to employee referrals to social media. But the efficacy of these approaches can be often debatable. But that’s a post for another day.
Here, we bring you some sure-fire concepts that will boost hiring efficiency.
Did you say mathematics?
Yes, you read it right. Mathematics! Perhaps the most hated subject ever, math can help recruiters solve one of the most prominent problems they face while trying to zero in on great talent.Let’s see how exactly it helps.
How many candidates should you interview before making a decision to hire? Imagine a situation where you have a hundred applicants for a position. The problem is that neither will you interview just one candidate nor will you interview all hundred. The dilemma is not whom to pick but how many to even consider before you hire (or you give up).
The most intuitive answer would be that it requires a balance between looking and leaping - that you must look at enough candidates to build a standard and decide on whatever satisfies the established standard. This looks like the perfect answer but here is the catch. Most people can’t say what this standard or balance should be. Luckily, mathematics comes to your rescue and provides the answer. Optimal Stopping Theory...
It is an idea “that every decision is a decision to stop what you are going to make a decision.”2 The theory suggests that you should reject the initial 37% of all the applicants and hire only after that. After this point, you should select the next applicant who is better than all candidates you interviewed before the cutoff. This is not intuition or a compromise between looking and leaping. It is a probable result.

Here look at this example if you have five weeks to choose a primary contractor. You could expect to see possibly four a week; that is an anticipated total of 20 suppliers. If you selected normally and selected the first ‘good enough’ option, the probability of finding the optimum supplier is just 5%. However, if you rejected the first 37% suppliers, in this case, 18 suppliers, and then selected the next supplier that was better than all the previous suppliers, then your odds of selecting the optimum supplier would increase to 40% (For the more curious people, go here to read about the famous example, the Secretary problem.)
This is just one of the mathematical theories that can help recruiters. To list a few more, there is Negativity Threshold which can help you identify the candidates that are inconsistent in their interview answers or are withholding information. Negativity Threshold was presented by Hannah Fry in her TED talk “The Mathematics of Love.” It was coined by John Gottman by observing how couples interact with each other.
The equations look something like this:
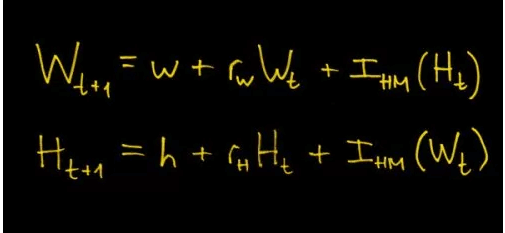
The left-hand side of the equation tells how positive or negative a wife/husband will be in the next thing she/he says. Here, w is the mood of the wife in general, r_w.W_t is the mood of the wife when she’s with her husband and I_(HM) is the influence that her husband’s actions will have on her. Researchers have plotted the effects the two partners have on each other. The plot looks as follows:

Here, the term T_ is the negativity threshold. At this point, the husband’s negative impact becomes so high that the wife responds with more negativity. To know more about this theory you can watch [ted talk link] or read this.
The negativity threshold suggests you be upfront about any issues and get all sorts of concerns out in open to avoid issues further down the line.
Another interesting equation that is worth looking at is The Drake Equation. The equation was conceived in 1961 by Dr. Frank Drake in an attempt to find the number of potential extraterrestrial bodies with life in the universe. He took something extremely complex and daunting and broke it down into something easy to understand. The Drake equation looks something like this:
N = R*•fp• ne• fl• fi• fc• L
The equation involves various factors such as the average rate of star formation in our galaxy, the fraction of stars that have formed planets, and much more which we will not get into. But, what how does this apply to hiring practices? A very obvious similarity is that both use data to pinpoint something or “someone” out there.
An important step in hiring candidates is determining the business factors your company wants to improve, says Emilio J. Castilla, Nanyang Technological University professor of management at the MIT Sloan School of Management. Determining these factors brings clarity to the business and helps everyone understand their roles. For instance, there is something called Sales Velocity, defined as:
Sales Velocity = Work In Progress ? Win Rate ? Avg. Deal Size ÷ Time Taken To Close
This equation does not help in identifying the top performers but also helps in determining the areas where an individual needs to improve. Drake’s theory is extremely useful when it comes to bringing order to a chaotic world.
Although most of the recruiting process is often dominated by emotion, mathematics is the one subject which can be applied everywhere, even hiring, without this particular bias.
Can you math enthusiasts think of any more? Let us know in Comments.
& for some of you who are super busy or are less inclined to "appreciating" math concepts, let us do the work for you.
Take a free trial for our Online Assessment software to hire the best mathematician (or developers) in your talent pipeline